DAG structure
DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph), is proposed again as a new underlying ledger structure. "Directed" refers to directional, "Acyclic" refers tonot cyclic,no return.
DAG model
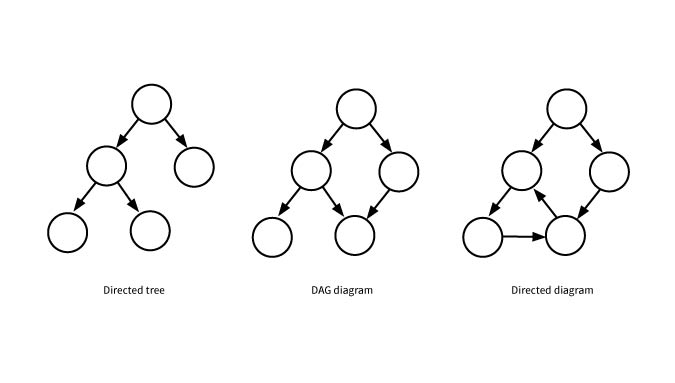
It’s obvious that the Merkle tree belongs to a type of directed tree structure, where each vertex in the tree can only point to one previous vertex, and the entire data has an obvious flow direction.DAG structure allows each vertex to point to multiple previous vertices, and the entire data flow has an obvious direction.Another data structure is directed graph, which is different from a DAG in that a directed graph allows data to flow back, and the data flow in the entire structure is not very clear. The differences among the three are shown in the figure.
Advantages of DAG structure
In DAG, there is no concept of block. Its constituent unit is a single transaction, which records the transaction of a single user. This eliminates the time needed to package blocks.The verification method depends on the verification of the previous transaction by the next transaction. In other words, to make a transaction, and the number of transactions to be verified depends on different rules. This verification method enables DAG to write many transactions asynchronously and concurrently, and ultimately forms a topological tree structure, which can greatly improve scalability.
In the context of blockchain, it is difficult to significantly improve scalability while ensuring decentralization and security, making it difficult to commercialize. DAG is decentralized in theory. If the network is powerful enough, the security can also be guaranteed, and more importantly, the scalability can be greatly improved.Distributed database with DAG technology can greatly improve transaction throughput and reduce transaction fees to a minimum.
DAG in blockchain
After having an intuitive understanding of the DAG structure, let's take a look at why blockchain is regarded as a special DAG structure?
According to the article "From Blockchain to DAG (I) - The Ledger Structure and Consensus Mechanism of Blockchain", whether the blockchain forks or not is related to the speed of generating blocks and broadcast speed. When the block generationspeed exceeds the broadcast speed, multiple blocks will be broadcast simultaneously, resulting in forks. The more forks there are, the lower the security is.In order to reduce forking,Bitcoin found a balance between performance and security by generating a block every ten minutes to reduce forks.Now let's assume that the block generation time is long enough to prevent a new block from being generated before the previous block has finished broadcasting.Then the structure of this blockchain is a single chain.
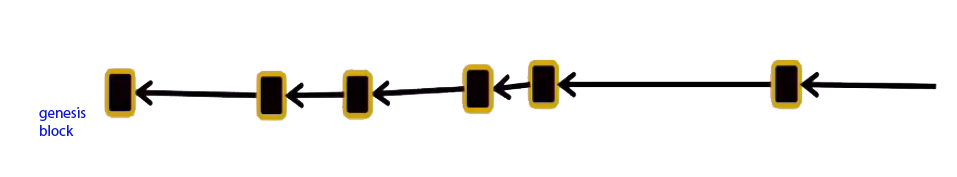
In fact, due to network latency and other reasons, forking is inevitable in blockchain, so the actual blockchain structure will be as shown in the figure, and only one valid main chain (yellow) will be selected through ledger consensus, and the transaction information in the remaining block (red) is invalid and will not be adopted.
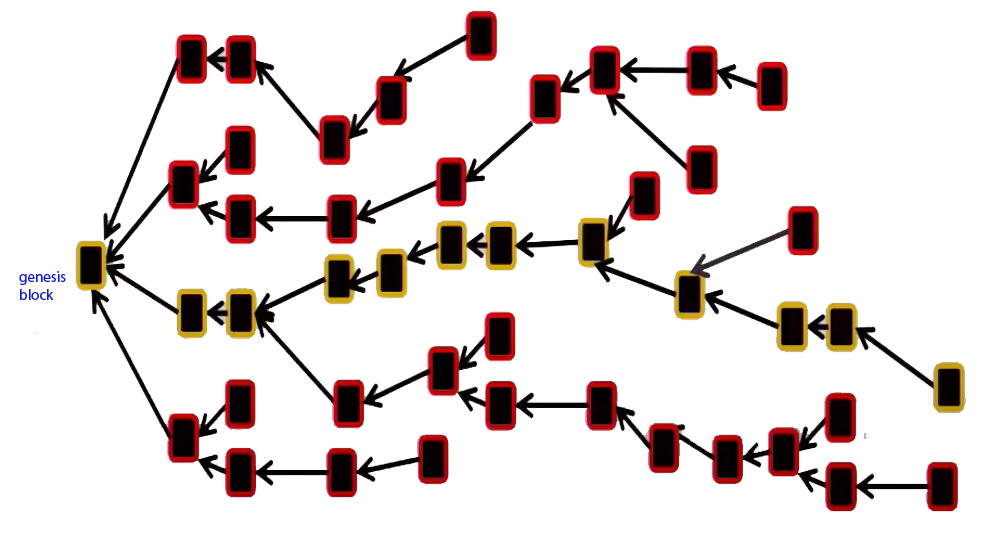 Transformers uses DAG structure to avoid the inability to concurrently execute block packaging in traditional blockchains.
If you change the chained storage structure of blocks into a DAG mesh topology, you can achieve concurrent writing.
In the case where the block packaging time remains unchanged, N blocks can be concurrently packaged in the network, and the transactions in the network can be increased by N times.
The combination of DAG and blockchain is to solve the efficiency problem. After the transaction is initiated, the network confirmation is broadcast directly.
From the perspective of the topology model above, the evolution from single chain to tree and mesh, from the granularity of blocks to the granularity of transactions, and from single point transitions to concurrent writing all enable transformers to make a qualitative leap in efficiency.
Transformers uses DAG structure to avoid the inability to concurrently execute block packaging in traditional blockchains.
If you change the chained storage structure of blocks into a DAG mesh topology, you can achieve concurrent writing.
In the case where the block packaging time remains unchanged, N blocks can be concurrently packaged in the network, and the transactions in the network can be increased by N times.
The combination of DAG and blockchain is to solve the efficiency problem. After the transaction is initiated, the network confirmation is broadcast directly.
From the perspective of the topology model above, the evolution from single chain to tree and mesh, from the granularity of blocks to the granularity of transactions, and from single point transitions to concurrent writing all enable transformers to make a qualitative leap in efficiency.